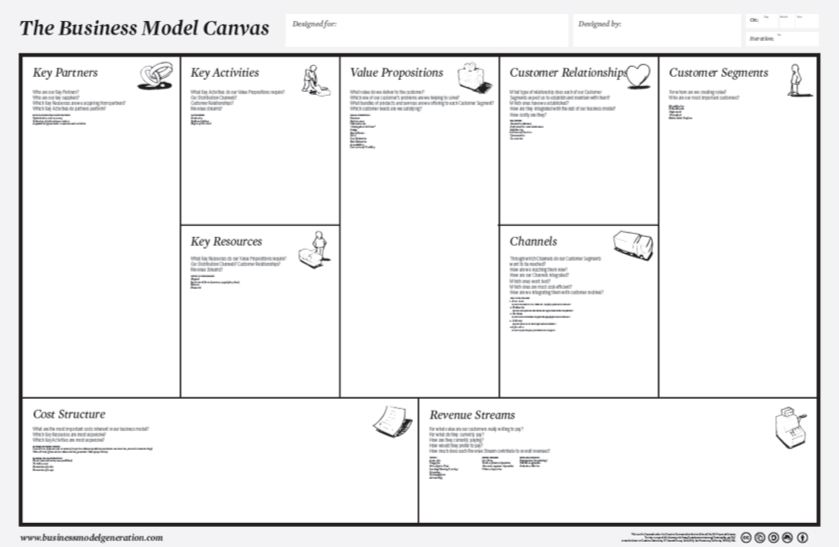
Business Model Canvas is a tool for working with the development of a business model, company or project.
The business Model Canvas template consists of a number of steps, or building blocks, that are mutually dependent and influencing each other. The template does not reflect a linear process, but it encourages the students to work with the different elements continually in an iterative process. It is an important point, when working with the Business Model Canvas, that all choices and changes are influencing the remaining building blocks.
You can use Business Model Canvas in your course as a reoccurring tool in which experiences, research results and data are documented. In that way the Business Model Canvas provides structure and ensures progress in the students’ project work.
Business Model Canvas is also described as a method, find the method description here.