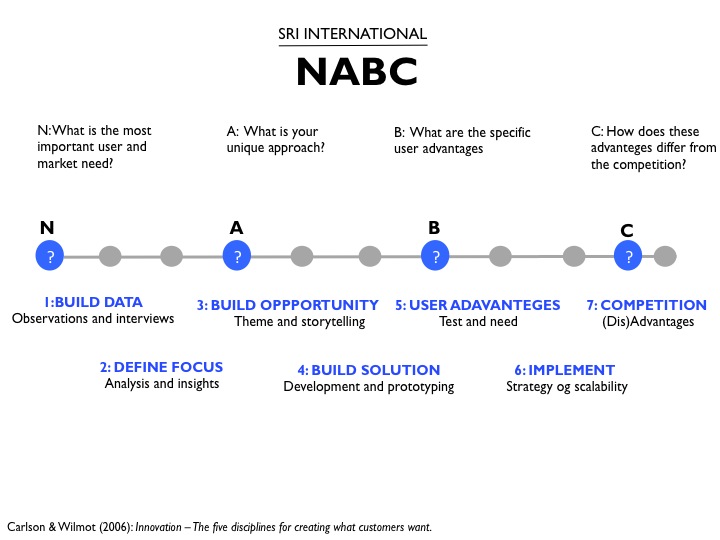
NABC’s fourth and final phase deals with the advantages and disadvantages of existing competition. You must answer this fundamental question: How does this idea and its benefits distinguish it from what competitors offer?
The idea you seek to realise should be able to succeed while competing for a user’s time and attention. Oftentimes, competition arises from similar goods and services offered by a competitor. However competition may present itself elsewhere, such as in a user’s hobbies or family patterns, habits, and routines. If the idea satisfies an important need, it is in itself a benefit to the user. So this phase is the moment to find the core aspect of your idea. That which is unique about your idea should be identified. Your idea’s core aspect should be so unique that it provides you with a competitive advantage.
This phase is characterised by an analytic and critical approach. In order to provide a convincing answer during the last two phases of the NABC model, it may be necessary to tweak your idea in a new direction. Perhaps new elements can be incorporated into the idea, making it more attractive for users. At the end of this phase you will present your idea for your customer/client or other party.